Electronic recordkeeping underpins modern apiary oversight. BeeGuard, Hive Tracks, and Blythewood Bee Company show how a subscription-based software system brings device feeds, weight trends, and anti-theft alerts into clear dashboards. This makes it easier to monitor hive health and respond fast.
Move away from paper to a reliable records system that saves accurate data in real time. Standardized entries let beekeepers track colony health, export CSVs for audits, and measure business outcomes over months and years.
Decide what each team member captures during a quick visit versus a full inspection. Clear scope and ownership reduce errors, save time, and improve operational value across hives and locations. Learn practical setup steps and examples in this guide, and review detailed recordkeeping practices at beekeeping records.
Key Takeaways
- Define scope: Make sure everyone knows what data to capture and why.
- Use software: It preserves records, enables exports, and speeds decisions.
- Integrate devices: Weather and weight sensors give timely, actionable insights.
- Balance visits: Capture essential fields on quick checks; expand during full inspections.
- Link to outcomes: Consistent data improves hive health monitoring and business planning.
Why digital field logs matter for better beekeeping today
Recording inspections in the cloud turns casual notes into consistent, comparable datasets that guide practical decisions.
From paper to cloud: turning inspections into actionable data
Shifting inspections from paper to a shared app produces consistent data that teams can analyze across the year. Hive Tracks emphasizes that standardized electronic records enable analytics, machine learning, and data mining to suggest treatments and queen selection.
Apps like those used by Blythewood Bee Company add precision, instant insights, and easy access. Cloud access lets teams update notes in real time, reducing missed treatments and redundant tasks.
Linking bee health, honey production, and business outcomes
Standardized records—inspections, treatments, queen status, and colony strength—turn raw information into usable insights.
- Real-time updates speed decisions during flows or disease events.
- Weather and microclimate data link to inspection notes to explain production shifts.
- Consistent history builds trendlines that improve health and forecast honey production.
| Benefit | Field Outcome | Business Result |
|---|---|---|
| Standardized records | Comparable hive status | Better planning, forecasting |
| Real-time cloud access | Faster interventions | Reduced losses, happier customers |
| Sensor integration | Contextualized production changes | Accurate yield estimates for buyers |
Planning your data: what to record, why it matters, and how it will be used
Start by deciding which pieces of hive data you must capture on every visit and which can be optional.
Core fields to capture
Record identifiers and location details so each hive stays traceable across seasons. Track hive ID, apiary location, and persistent equipment tags.
Log queen attributes (lineage, color), colony strength (brood frames, food stores), treatments, sanitary tests (Varroa, VP100), feedings, harvests, and transhumance events. These entries link directly to operational choices and health outcomes.
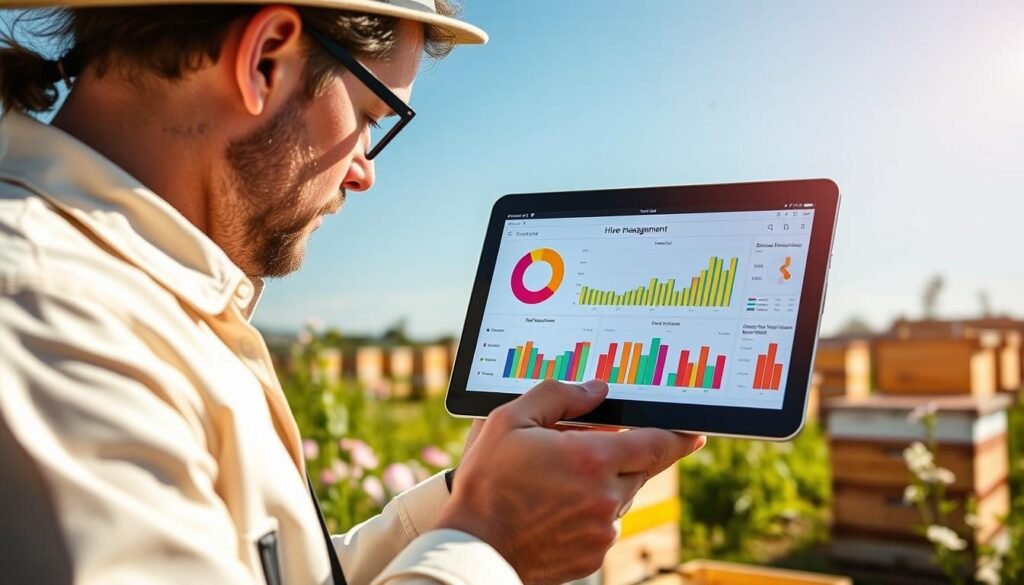

Designing a schema that supports decisions
Specify required vs. optional fields. Use controlled vocabularies and dropdowns to keep records consistent across users.
“Standardized entries convert routine checks into analytics-ready information.”
- Map each field to its decision use-case (inspections → treatments, queen history → temperament).
- Build validation rules to prevent missing or conflicting entries.
- Plan persistent IDs and link movements to production and health results.
| Field | Required? | Decision Use |
|---|---|---|
| Hive ID | Yes | Track lineage, equipment, history |
| Queen (lineage/color) | Yes | Breeding, temperament, replacement timing |
| Brood frames / Food stores | Yes | Feeding, split, harvest planning |
| Sanitary tests (Varroa, VP100) | Optional but recommended | Mite thresholds, treatment timing |
Test the schema with real visits to ensure data entry stays fast. Tools like BeeGuard and Hive Tracks support detailed visit levels and standardized formats, helping a beekeeper scale records without slowing inspections. Align your schema with reporting needs and define who can edit records to protect data integrity. For seasonal task alignment, see seasonal beekeeping tasks.
Choosing the right tools: apps and software that power apiary management
Pick tools that match how your crews work so data flows into useful dashboards without extra steps.
BeeGuard overview: sensors, dashboards, maps, and exportable records
BeeGuard is an annual subscription software that ties weather, hive weight variation, and anti-theft alerts into unified maps and tables.
The platform offers 7- and 30-day views, configurable visualization windows, and three navigation modes: apiary maps, map view, and table view. It logs visits and actions like transhumance, queen color, brood frames, Varroa and VP100 tests, feedings, and harvests.
Exports are Excel/CSV and data retention is unlimited while subscribed, making audits and analysis straightforward.
Hive Tracks focus: standardized electronic records that enable insights
Hive Tracks emphasizes standardized records to feed analytics and lifecycle-driven insights.
Teams use it when they need structured entries that support machine learning, long-term trendlines, and consistent inspections and treatments tracking.
Other apps and matching features to your operation
Blythewood Bee Company highlights options such as BeePlus, Apiary Book, HiveTool Mobile, BeeScanning, Beekeeper’s Companion, and BeeCheck.
When you evaluate tools, confirm:
- Device integration (weather, weights, anti-theft) and clear 7‑ or 30‑day dashboards.
- Offline capture, fast checklists for inspections and treatments, and photo attachments.
- Scalability across locations and hives, with user roles for beekeepers and managers.
- Easy exports and interoperable formats to avoid vendor lock-in.
“Choose tools whose navigation modes mirror your yard layout and daily routes.”
| Need | Recommended | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Many sites & hives | Table view + maps | Faster planning and batch updates |
| Analytics & forecasting | Standardized records (Hive Tracks) | Feeds models and trend reports |
| Field speed | Offline capture, one-tap updates | Reduces entry errors during inspections |
Setting up your system for Creating digital field logs for apiary management
Start with a clear map and naming rules so hives and reports match at the gate and in the app.
Configuring apiaries, devices, and navigation views
Structure locations and apiaries first. Align naming with physical signage so each hive ID in the system matches equipment in the yard.
Connect weather stations, weight scales, and anti-theft devices to your software. This streams alerts and weight trends into 7- and 30-day dashboards without manual entry.
Choose default views: apiary maps for yard planning, map view for routing across location points, and table view when you manage many hives and tasks at once.
Customizing inspection templates
Build templates that list brood frames, queen status, Varroa and VP100 tests, feedings, and harvests. Add quick toggles to speed one-minute checks on busy days.
Include conditional prompts. If mite counts exceed thresholds, suggest treatments so actions stay consistent across the colony and crew.
Establishing data governance and backups
Define roles and who can create, edit, or delete records. Set access rules and approval steps for sensitive entries like treatments and harvest weights.
“Schedule routine exports and test restores so last year’s records are always recoverable.”
| Setup Step | Why it matters | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Naming conventions | Prevents mismatched IDs | Match signs to system labels |
| Device integration | Timely alerts and trends | Connect weather, scales, anti-theft |
| Templates & prompts | Standardizes inspections | Include brood, queen, tests, feedings |
| Governance & backups | Data integrity and audits | Role limits, exports, restore tests |
Pilot the setup in one location, collect feedback from beekeepers, then scale. For deeper guidance on electronic recordkeeping, see electronic recordkeeping.
Field workflows that save time and capture the right information
Smart visit modes save time by letting beekeepers choose how much detail each stop requires.
BeeGuard lets teams set visit precision — from a date-only quick check to a full inspection that logs frames, queen notes, tests, photos, and treatments. This flexibility keeps crews moving while keeping accurate records where it matters.

Quick-entry vs. detailed visits: when to go light and when to go deep
Define two visit modes. Quick-entry captures date, weather, and basic brood or food status. Detailed inspections record full frames, queen status, tests, photos, and any treatments applied.
Use the app checklists to standardize inspections so beekeepers complete key tasks and log exceptions for follow-up. Capture minimal records on busy days, then schedule deeper visits for flagged hives.
Applying simultaneous actions at the apiary level to streamline operations
Apply actions across an entire apiary — feed, equalize, or add supers — to save time and keep records consistent. Batch updates (for example, mark many hives as treated) speed repetitive tasks while still allowing single-hive notes when needed.
- Trigger follow-up tasks automatically from inspection results.
- Use device data to prioritize urgent hives by weight or temp anomalies.
- Tag photos and voice notes so context stays with each entry.
Review daily entries before leaving the yard to fix errors and keep the operation ready for reporting and analysis. Learn more about useful beekeeping technologies that speed these workflows.
Turn records into insights: using your logs to improve bee health and production
Use short time-window views to catch sudden shifts in weight, flight activity, or weather that need action now. BeeGuard supplies configurable 7‑ and 30‑day dashboards with device-driven metrics like weather, hive weight variation, and anti‑theft alerts. Those views make it simple to spot spikes and act quickly.
Dashboards and time windows
View trends over 7 or 30 days to translate anomalies into immediate steps. A quick rise in weight may signal a nectar flow; a sudden drop plus poor weather can prompt inspections.
Information Systems Lifecycle
Remember the past, prepare the future, optimize the present. Hive Tracks frames this lifecycle: analyze past records, model likely outcomes, and run targeted actions while monitoring effects in real time.
Exports and reporting
Export clean Excel/CSV datasets to build custom reports for customers, insurers, and regulators. Clean exports let you prove compliance, show service quality, and quantify outcomes like increased harvest weight.
- Blend inspection notes with device data to prioritize treatments without harming production.
- Segment insights by locations and apiary to refine playbooks year over year.
- Benchmark hives to measure value from queen selection and nutrition plans.
- Schedule recurring insight reviews so beekeepers align on decisions and improve consistency.
“Leverage alerts tied to weather and weight variation to catch early warnings and schedule proactive responses.”
For deeper reading on recordkeeping and analysis, see beekeeping resources and books.
Conclusion
Standardized records and sensor feeds make each hive’s story measurable and actionable.
Commit to digital field records as the operational backbone that aligns beekeeping practices with measurable outcomes for each hive and apiary. Clear schemas, chosen software and configured locations keep teams moving and reduce errors.
Complete data and consistent records let beekeepers manage proactively, speed audits, and show value in harvests and service. Good governance and routine exports lower risk and speed decision-making during peak seasons.
Start small: define fields, pick software that fits your operation, set views, and train crews. Over time disciplined management across locations compounds into stronger insights, healthier bee colonies, and steadier honey production.
Learn more about precision systems and sensor architecture at precision beekeeping research. Choose tools, set standards, and let your data guide daily work and long-term strategy with confidence.
FAQ
What are digital field logs and how do they help beekeepers?
Digital field logs are electronic records that replace paper notes and capture inspections, treatments, harvests, and location data. They help beekeepers track hive health, queen status, Varroa counts, and feedings over time so you can spot trends, make informed decisions, and improve honey production and colony survival.
How do I move from paper notebooks to a cloud-based system without losing data?
Start by standardizing the key fields you record on paper (hive ID, location, date, notes, treatments, queen info). Choose a platform that supports CSV imports or manual bulk entry. Migrate recent records first, then archive older notes. Test exports and backups to ensure nothing is lost during transfer.
What core data points should every inspection include?
Each inspection should capture hive ID, apiary location, date/time, inspector name, brood pattern, queen presence or status, Varroa test result, food stores, signs of disease, treatments applied, and action items. These fields support health tracking, regulatory reporting, and production forecasting.
How can I design a schema that supports future analytics?
Use consistent field names, enforce controlled lists for values (e.g., treatment types, disease codes), include timestamps and GPS coordinates, and link records to unique hive and apiary IDs. This structure enables trend analysis, filtering, and machine-readable exports for advanced analytics.
Which apps and software are commonly used for hive records and why?
Popular tools include HiveTracks for standardized electronic records and BeeGuard for sensor integration and dashboards. Look for features like offline entry, GPS mapping, exportable reports, role-based access, and integration with weather or sensors to support operational needs.
How do I choose the right tool for my operation size and locations?
Match features to your needs: small operations may prioritize low cost and simple mobile entry; commercial operations need multi-user access, bulk actions, device integrations, and analytics. Consider number of apiaries, remote locations, and whether you need customer or regulator reporting.
What device integrations should I consider when setting up the system?
Consider GPS-enabled mobile apps for precise locations, hive scales for weight and feeding status, environmental sensors for temperature and humidity, and Varroa counters if available. Ensure the platform supports data sync, offline mode, and export routines for backups.
How should I customize inspection templates for consistency?
Create templates that include required fields (e.g., queen status, brood frames, Varroa test, feedings) and optional notes. Use checklists and dropdowns to reduce free text. Tailor templates by season or task (spring build-up, summer inspection, fall wrap-up) to streamline entry.
What are best practices for data governance and backups?
Define user roles and access levels, require authentication, and maintain an export schedule (daily/weekly). Keep off-site backups, version exports in standard formats (CSV, JSON), and document data retention policies to meet customer, insurer, or regulatory needs.
When should I perform quick-entry visits versus detailed inspections?
Use quick-entry for routine checks like weight, activity, and obvious queen presence when managing many sites or after a major operation. Reserve detailed inspections for suspected health issues, seasonal assessments, queen introductions, or pre-harvest checks to capture full diagnostics.
How can simultaneous actions at the apiary level save time?
Apply actions like treatments, feeds, or notes across multiple hives at once when the condition affects the entire apiary. Bulk scheduling and templated notes reduce redundant entry and ensure consistent records for groups of colonies.
What dashboard views are most useful to monitor trends?
Use 7-day and 30-day views to detect short-term shifts and seasonal trends. Include weight, Varroa counts, brood status, and inspection frequency. Filter by apiary, queen line, or treatment to isolate causes and measure treatment effectiveness over time.
How do I export data for analysis, customers, or regulators?
Export in common formats like CSV or JSON and include metadata (timestamps, GPS, inspector). Provide summary reports for customers or regulators and detailed records for insurers. Automate scheduled exports and keep an archive for audit trails.
Can records improve honey production and colony health over time?
Yes. Consistent records reveal patterns in queen performance, disease cycles, and environmental impacts. Use insights to time interventions, optimize feeding and harvesting, and prioritize hives for requeening or treatment, which raises overall productivity and value.
What common mistakes should I avoid when starting electronic hive records?
Avoid inconsistent field names, excessive free-text fields, lack of backups, and no user permissions. Don’t skip training—make sure all users follow templates. Also avoid overloading records with unnecessary fields that reduce adoption and slow inspections.
How do weather and location data integrate with hive records?
Link records to local weather data and GPS locations to correlate colony behavior with temperature, precipitation, and bloom periods. This helps explain sudden weight changes, forage availability, and disease outbreaks, improving timing for treatments and harvests.
What features should I prioritize if I need to report to customers or buyers?
Prioritize exportable harvest records, traceability by hive or lot, treatment histories, and quality notes. Generate concise reports showing origin, inspection dates, and test results to build buyer trust and meet food safety or certification requirements.